这篇文章主要对应王道P221上面的第四题和第五题
- 第四题:分别采用基于DFS和BFS算法,判别以邻接表方式存储的有向图中是否存在由顶点\(V_i\)到顶点\(V_j\)的路径。
- 第五题:假设图用邻接表表示,设计一个算法,输出从顶点到顶点\(V_i\)到顶点\(V_j\)的
所有简单路径 - 文章的代码都为有向图,无向图的算法一样,只是创建不同,可以看看我前面写的
第四题
DFS方法
第四题分析:我们知道,DFS(G, i)表示在图G中,从顶点i开始,进行一次深搜,深搜结束后,顶点i所在的连通块会被全部访问完毕,那么也就是说我们可以从\(V_i\)这个顶点开始进行一次深搜,结束后看看\(V_j\)这个顶点有无被访问过,这个方法比较暴力,也是我第一眼看到这个题之后想到的算法(因为DFS的代码之前就已经写好了hh),代码如下:
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
//邻接表从起点i开始的深度优先搜索
void DFS(ALGraph G, int i) { //DFS每次会搜索一个连通图
ArcNode * p;
visited[i] = true;
p = G.vertices[i].first;
while(p) {
if(!visited[p -> adjvex]) {
DFS(G, p -> adjvex);
}
p = p -> next;
}
}
//判断vi和vj是否连通
bool ExistPath_DFS(ALGraph G, int vi, int vj) {
DFS(G, vi);
return visited[vj]; //如果vj被访问过,那么就说明有路径,
}这个方法其实比较暴力,每次运行都是最坏情况,其实我们可以在进行DFS的过程中进行判断,如果正在访问的顶点是\(V_j\),那么说明有路径,直接返回即可,如果DFS执行完还没有被访问过,那就说明没有路径。
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
//邻接表从起点i开始的深度优先搜索
bool ExistPath_DFS(ALGraph G, int vi, int vj) { //DFS每次会搜索一个连通图,也就是说,调用dfs的次数,取决于连通块的个数
ArcNode * p;
visited[vi] = true;
if(vi == vj) return true;
p = G.vertices[vi].first;
while(p) {
if(!visited[p -> adjvex] && ExistPath_DFS(G, p -> adjvex, vj)) {
return true;
}
p = p -> next;
}
return false;
}方法一全部代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxVertexNum 100
#define VertexType char
//边表结点
typedef struct ArcNode {
int adjvex; //存储该结点在顶点表中的下标
ArcNode * next; //指向下一个边表
}ArcNode;
//顶点表结点
typedef struct VNode {
VertexType data; //顶点信息
ArcNode * first; //指向边表
} VNode, AdjList[MaxVertexNum]; //顶点和顶点表
//图的存储结构
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices; //邻接表
int vertexnum, arcnum; //维护图的顶点数和边的个数
} ALGraph;
//找到结点x在顶点表中的位置
int LocateVex(ALGraph & G, VertexType x) {
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; i ++) {
if(x == G.vertices[i].data)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void CreateALGrapha(ALGraph & G) {
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:";
cin >> G.vertexnum >> G.arcnum;
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; ++i) {
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "个顶点的信息:";
cin >> G.vertices[i].data;
G.vertices[i].first = NULL;
}
for(int i = 0; i < G.arcnum; ++i) {
VertexType e1, e2;
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "条边的顶点:";
cin >> e1 >> e2;
ArcNode * e = new ArcNode;
if(!e) {
cout << "内存分配失败:" << endl;
exit(0);
}
int vi = LocateVex(G, e1);
int vj = LocateVex(G, e2);
//e1和e2之间有一条边,先用头插法将e2的边表插到e1的顶点表后,无向图,只用创建一条边
e -> adjvex = vj;
e -> next = G.vertices[vi].first;
G.vertices[vi].first = e;
}
}
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
//邻接表从起点i开始的深度优先搜索
void DFS(ALGraph G, int i) { //DFS每次会搜索一个连通图,也就是说,调用dfs的次数,取决于连通块的个数
ArcNode * p;
visited[i] = true;
p = G.vertices[i].first;
while(p) {
if(!visited[p -> adjvex]) {
DFS(G, p -> adjvex);
}
p = p -> next;
}
}
bool ExistPath_DFS(ALGraph G, int vi, int vj) {
DFS(G, vi);
return visited[vj];
}
int main() {
ALGraph G;
CreateALGrapha(G);
VertexType a, b;
cout << "输入两个顶点:" << endl;
cin >> a >> b;
if(ExistPath_DFS(G, LocateVex(G, a), LocateVex(G, b))) {
cout << "存在" << endl;
} else {
cout << "不存在" << endl;
}
}
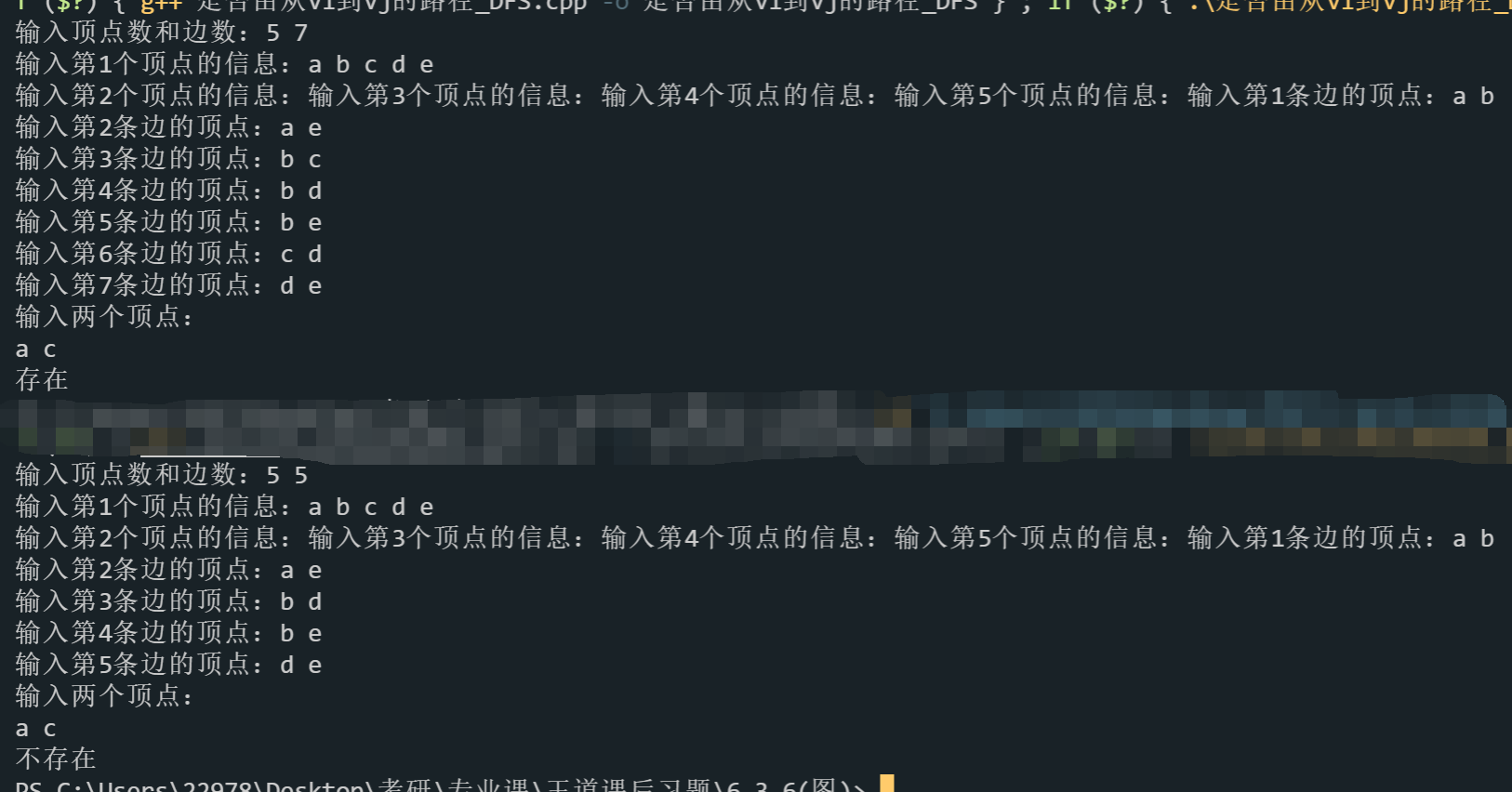
/*
输入序列(路径存在)
5 7
a b c d e
a b
a e
b c
b d
b e
c d
d e
a c
(路径不存在)
5 5
a b c d e
a b
a e
b d
b e
d e
a c
*/方法二全部代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxVertexNum 100
#define VertexType char
//边表结点
typedef struct ArcNode {
int adjvex; //存储该结点在顶点表中的下标
ArcNode * next; //指向下一个边表
}ArcNode;
//顶点表结点
typedef struct VNode {
VertexType data; //顶点信息
ArcNode * first; //指向边表
} VNode, AdjList[MaxVertexNum]; //顶点和顶点表
//图的存储结构
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices; //邻接表
int vertexnum, arcnum; //维护图的顶点数和边的个数
} ALGraph;
//找到结点x在顶点表中的位置
int LocateVex(ALGraph & G, VertexType x) {
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; i ++) {
if(x == G.vertices[i].data)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void CreateALGrapha(ALGraph & G) {
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:";
cin >> G.vertexnum >> G.arcnum;
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; ++i) {
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "个顶点的信息:";
cin >> G.vertices[i].data;
G.vertices[i].first = NULL;
}
for(int i = 0; i < G.arcnum; ++i) {
VertexType e1, e2;
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "条边的顶点:";
cin >> e1 >> e2;
ArcNode * e = new ArcNode;
if(!e) {
cout << "内存分配失败:" << endl;
exit(0);
}
int vi = LocateVex(G, e1);
int vj = LocateVex(G, e2);
//e1和e2之间有一条边,先用头插法将e2的边表插到e1的顶点表后
e -> adjvex = vj;
e -> next = G.vertices[vi].first;
G.vertices[vi].first = e;
}
}
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
bool ExistPath_DFS(ALGraph G, int vi, int vj) {
ArcNode * p;
visited[vi] = true;
if(vi == vj) return true;
p = G.vertices[vi].first;
while(p) {
if(!visited[p -> adjvex] && ExistPath_DFS(G, p -> adjvex, vj)) {
return true;
}
p = p -> next;
}
return false;
}
int main() {
ALGraph G;
CreateALGrapha(G);
VertexType a, b;
cout << "输入两个顶点:" << endl;
cin >> a >> b;
if(ExistPath_DFS(G, LocateVex(G, a), LocateVex(G, b))) {
cout << "存在" << endl;
} else {
cout << "不存在" << endl;
}
}
/*
输入序列(路径存在)
5 7
a b c d e
a b
a e
b c
b d
b e
c d
d e
a c
(路径不存在)
5 5
a b c d e
a b
a e
b d
b e
d e
a c
*/BFS方法
方法一和DFS的方法一一样,跑完一次BFS之后看看\(V_j\)是否被访问过
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
void BFS(ALGraph G, int i) {
cout << G.vertices[i].data << endl;
visited[i] = true;
Queue que;
que.front = que.rear = que.tag = 0;
EnQueue(que, i);
while(!(que.front == que.rear && que.tag == 0)) { //若队列非空
int p;
DeQueue(que, p);
//将p有关系的结点加入队列中
ArcNode * cur = G.vertices[p].first;
while(cur) {
if(!visited[cur -> adjvex]) {
EnQueue(que, cur -> adjvex);
visited[cur -> adjvex] = true;
}
cur = cur -> next;
}
}
}
bool ExistPath_BFS(ALGraph G, int vi, int vj) {
BFS(G, vi);
return visited[vj];
}方法二,在BFS的中途判断看当前所访问的结点是否是\(V_j\)
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
bool ExistPath_BFS(ALGraph G, int vi, int vj) {
visited[vi] = true;
Queue que;
que.front = que.rear = que.tag = 0;
EnQueue(que, vi);
while(!(que.front == que.rear && que.tag == 0)) { //若队列非空
int p;
DeQueue(que, p);
if(p == vj) return true;
//将p有关系的结点加入队列中
ArcNode * cur = G.vertices[p].first;
while(cur) {
if(!visited[cur -> adjvex]) {
EnQueue(que, cur -> adjvex);
visited[cur -> adjvex] = true;
}
cur = cur -> next;
}
}
return false;
}
方法一全部代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxVertexNum 100
#define VertexType char
//边表结点
typedef struct ArcNode {
int adjvex; //存储该结点在顶点表中的下标
ArcNode * next; //指向下一个边表
}ArcNode;
//顶点表结点
typedef struct VNode {
VertexType data; //顶点信息
ArcNode * first; //指向边表
} VNode, AdjList[MaxVertexNum]; //顶点和顶点表
//图的存储结构
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices; //邻接表
int vertexnum, arcnum; //维护图的顶点数和边的个数
} ALGraph;
//队列:
typedef struct Queue {
int data[MaxVertexNum];
int front, rear, tag;
} Queue;
bool EnQueue(Queue & que, int p) {
if(que.rear == que.front && que.tag == 1) {
cout << "Queue is full!" << endl;
return false;
}
que.data[que.rear] = p;
que.rear = (que.rear + 1) % MaxVertexNum;
que.tag = 1;
return true;
}
bool DeQueue(Queue & que, int & p) {
if(que.front == que.rear && que.tag == 0) {
cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl;
return false;
}
p = que.data[que.front];
que.front = (que.front + 1) % MaxVertexNum;
que.tag = 0;
return true;
}
//找到结点x在顶点表中的位置
int LocateVex(ALGraph & G, VertexType x) {
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; i ++) {
if(x == G.vertices[i].data)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void CreateALGrapha(ALGraph & G) {
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:";
cin >> G.vertexnum >> G.arcnum;
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; ++i) {
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "个顶点的信息:";
cin >> G.vertices[i].data;
G.vertices[i].first = NULL;
}
for(int i = 0; i < G.arcnum; ++i) {
VertexType e1, e2;
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "条边的顶点:";
cin >> e1 >> e2;
ArcNode * e = new ArcNode;
if(!e) {
cout << "内存分配失败:" << endl;
exit(0);
}
int vi = LocateVex(G, e1);
int vj = LocateVex(G, e2);
//e1和e2之间有一条边,先用头插法将e2的边表插到e1的顶点表后
e -> adjvex = vj;
e -> next = G.vertices[vi].first;
G.vertices[vi].first = e;
e = new ArcNode;
if(!e) {
cout << "内存分配失败:" << endl;
exit(0);
}
//再将e1的边表插到e2的顶点表
e -> adjvex = vi;
e -> next = G.vertices[vj].first;
G.vertices[vj].first = e;
}
}
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
void BFS(ALGraph G, int i) {
cout << G.vertices[i].data << endl;
visited[i] = true;
Queue que;
que.front = que.rear = que.tag = 0;
EnQueue(que, i);
while(!(que.front == que.rear && que.tag == 0)) { //若队列非空
int p;
DeQueue(que, p);
//将p有关系的结点加入队列中
ArcNode * cur = G.vertices[p].first;
while(cur) {
if(!visited[cur -> adjvex]) {
EnQueue(que, cur -> adjvex);
visited[cur -> adjvex] = true;
}
cur = cur -> next;
}
}
}
bool ExistPath_BFS(ALGraph G, int vi, int vj) {
BFS(G, vi);
return visited[vj];
}
int main() {
ALGraph G;
CreateALGrapha(G);
VertexType a, b;
cout << "输入两个顶点:" << endl;
cin >> a >> b;
if(ExistPath_BFS(G, LocateVex(G, a), LocateVex(G, b))) {
cout << "存在" << endl;
} else {
cout << "不存在" << endl;
}
}
/*
输入序列
(路径存在)
5 7
a b c d e
a b
a e
b c
b d
b e
c d
d e
a c
(路径不存在)
5 5
a b c d e
a b
a e
b d
b e
d e
a c
*/全部代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxVertexNum 100
#define VertexType char
//边表结点
typedef struct ArcNode {
int adjvex; //存储该结点在顶点表中的下标
ArcNode * next; //指向下一个边表
}ArcNode;
//顶点表结点
typedef struct VNode {
VertexType data; //顶点信息
ArcNode * first; //指向边表
} VNode, AdjList[MaxVertexNum]; //顶点和顶点表
//图的存储结构
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices; //邻接表
int vertexnum, arcnum; //维护图的顶点数和边的个数
} ALGraph;
//队列:
typedef struct Queue {
int data[MaxVertexNum];
int front, rear, tag;
} Queue;
bool EnQueue(Queue & que, int p) {
if(que.rear == que.front && que.tag == 1) {
cout << "Queue is full!" << endl;
return false;
}
que.data[que.rear] = p;
que.rear = (que.rear + 1) % MaxVertexNum;
que.tag = 1;
return true;
}
bool DeQueue(Queue & que, int & p) {
if(que.front == que.rear && que.tag == 0) {
cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl;
return false;
}
p = que.data[que.front];
que.front = (que.front + 1) % MaxVertexNum;
que.tag = 0;
return true;
}
//找到结点x在顶点表中的位置
int LocateVex(ALGraph & G, VertexType x) {
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; i ++) {
if(x == G.vertices[i].data)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void CreateALGrapha(ALGraph & G) {
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:";
cin >> G.vertexnum >> G.arcnum;
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; ++i) {
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "个顶点的信息:";
cin >> G.vertices[i].data;
G.vertices[i].first = NULL;
}
for(int i = 0; i < G.arcnum; ++i) {
VertexType e1, e2;
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "条边的顶点:";
cin >> e1 >> e2;
ArcNode * e = new ArcNode;
if(!e) {
cout << "内存分配失败:" << endl;
exit(0);
}
int vi = LocateVex(G, e1);
int vj = LocateVex(G, e2);
//e1和e2之间有一条边,先用头插法将e2的边表插到e1的顶点表后
e -> adjvex = vj;
e -> next = G.vertices[vi].first;
G.vertices[vi].first = e;
e = new ArcNode;
if(!e) {
cout << "内存分配失败:" << endl;
exit(0);
}
//再将e1的边表插到e2的顶点表
e -> adjvex = vi;
e -> next = G.vertices[vj].first;
G.vertices[vj].first = e;
}
}
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
bool ExistPath_BFS(ALGraph G, int vi, int vj) {
visited[vi] = true;
Queue que;
que.front = que.rear = que.tag = 0;
EnQueue(que, vi);
while(!(que.front == que.rear && que.tag == 0)) { //若队列非空
int p;
DeQueue(que, p);
if(p == vj) return true;
//将p有关系的结点加入队列中
ArcNode * cur = G.vertices[p].first;
while(cur) {
if(!visited[cur -> adjvex]) {
EnQueue(que, cur -> adjvex);
visited[cur -> adjvex] = true;
}
cur = cur -> next;
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
ALGraph G;
CreateALGrapha(G);
VertexType a, b;
cout << "输入两个顶点:" << endl;
cin >> a >> b;
if(ExistPath_BFS(G, LocateVex(G, a), LocateVex(G, b))) {
cout << "存在" << endl;
} else {
cout << "不存在" << endl;
}
}
/*
输入序列
(路径存在)
5 7
a b c d e
a b
a e
b c
b d
b e
c d
d e
a c
(路径不存在)
5 5
a b c d e
a b
a e
b d
b e
d e
a c
*/
第五题
这道题直接使用DFS进行搜索就好了,只是在DFS的过程中,需要使用一个数组来记录已经访问过的的结点,如果当前访问的结点正好是\(V_j\),那么就将数组中所存放的全部历史访问结点都输出,这道题我感觉比较难的地方就在于怎样使用数组来维护正在访问的结点,流程和其他DFS搜索的题其实大同小异。比方说这些题。
- \(V_i\)表示当前正在访问的结点
- \(V_j\)表示目标结点
- path数组用于存放当前正在访问的结点
- now类似栈顶指针
void PrintPath_DFS (ALGraph G, int vi, int vj, int path[], int now) {
visited[vi] = true;
path[now ++] = vi; //将当前正访问的结点加入path数组中
if(vi == vj) { //如果已经访问到目标结点
for(int i = 0; i < now; ++i) { //输出当前数组中的所有结点
cout << G.vertices[path[i]].data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
ArcNode * p = G.vertices[vi].first;
while(p) {
if(!visited[p -> adjvex]) {
PrintPath_DFS(G, p -> adjvex, vj, path, now);
}
p = p -> next;
}
visited[vi] = false; //恢复现场,因为要输出所有的路径
}全部代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxVertexNum 100
#define VertexType char
//边表结点
typedef struct ArcNode {
int adjvex; //存储该结点在顶点表中的下标
ArcNode * next; //指向下一个边表
}ArcNode;
//顶点表结点
typedef struct VNode {
VertexType data; //顶点信息
ArcNode * first; //指向边表
} VNode, AdjList[MaxVertexNum]; //顶点和顶点表
//图的存储结构
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices; //邻接表
int vertexnum, arcnum; //维护图的顶点数和边的个数
} ALGraph;
//找到结点x在顶点表中的位置
int LocateVex(ALGraph & G, VertexType x) {
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; i ++) {
if(x == G.vertices[i].data)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void CreateALGrapha(ALGraph & G) {
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:";
cin >> G.vertexnum >> G.arcnum;
for(int i = 0; i < G.vertexnum; ++i) {
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "个顶点的信息:";
cin >> G.vertices[i].data;
G.vertices[i].first = NULL;
}
for(int i = 0; i < G.arcnum; ++i) {
VertexType e1, e2;
cout << "输入第" << i + 1 << "条边的顶点:";
cin >> e1 >> e2;
ArcNode * e = new ArcNode;
if(!e) {
cout << "内存分配失败:" << endl;
exit(0);
}
int vi = LocateVex(G, e1);
int vj = LocateVex(G, e2);
//e1和e2之间有一条边,先用头插法将e2的边表插到e1的顶点表后
e -> adjvex = vj;
e -> next = G.vertices[vi].first;
G.vertices[vi].first = e;
e = new ArcNode;
if(!e) {
cout << "内存分配失败:" << endl;
exit(0);
}
//再将e1的边表插到e2的顶点表
e -> adjvex = vi;
e -> next = G.vertices[vj].first;
G.vertices[vj].first = e;
}
}
bool visited[MaxVertexNum];
void PrintPath_DFS (ALGraph G, int vi, int vj, int path[], int now) {
visited[vi] = true;
path[now ++] = vi;
if(vi == vj) {
for(int i = 0; i < now; ++i) {
cout << G.vertices[path[i]].data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
ArcNode * p = G.vertices[vi].first;
while(p) {
if(!visited[p -> adjvex]) {
PrintPath_DFS(G, p -> adjvex, vj, path, now);
}
p = p -> next;
}
visited[vi] = false;
}
int main() {
ALGraph G;
CreateALGrapha(G);
VertexType a, b;
cout << "输入两个顶点:";
cin >> a >> b;
int path[10000];
PrintPath_DFS(G, LocateVex(G, a), LocateVex(G, b), path, 0);
return 0;
}
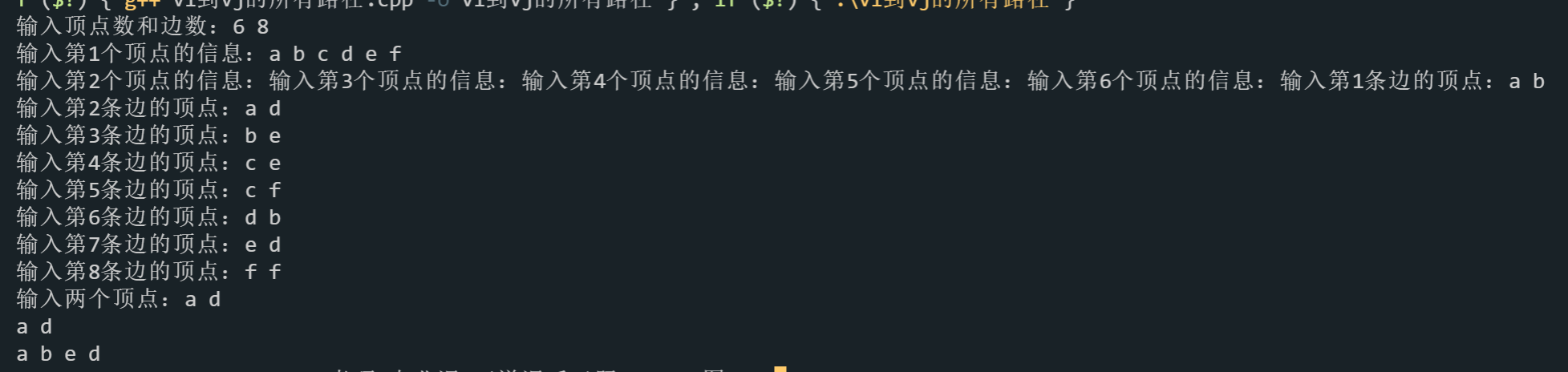
/*
输入序列
6 8
a b c d e f
a b
a d
b e
c e
c f
d b
e d
f f
*/






Comments 2 条评论
前排
@匿名 没人和你抢